Implementing Transfer Learning with VGG 16
Leveraging Pre-trained Models for Specific Tasks
 Program output
Program outputTransfer Learning with VGG 16 Model
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Steps
- Step 1: Explore the VGG 16 model and the data it is trained on
- Step 2: Load the VGG 16 model in your notebook and print the summary of the model
- Step 3: Load a few images in your notebook and predict the class
- Step 4: Explore how to remove the last layer of the VGG model
- Step 5: Add a few layers to the VGG 16 model
- Step 6: Add binary classification data and compile the model
- Step 7: Train the new model for binary classification of images
- Step 8: Define the layers which are trainable
Introduction
This README provides a structured guide for implementing Transfer Learning with the VGG 16 model. Transfer learning allows us to leverage pre-trained models like VGG 16, which is trained on large-scale image datasets like ImageNet, and adapt them for specific tasks with relatively smaller datasets.
Steps
Step 1: Explore the VGG 16 model and the data it is trained on
Explore the architecture and details of the VGG 16 model, as well as the ImageNet dataset it is trained on.
Step 2: Load the VGG 16 model in your notebook and print the summary of the model
Step 2a: Load an image from file and pre-process it
Load an image from a file, preprocess it according to the requirements of the VGG 16 model (e.g., resize, normalization), and prepare it for inference.
Step 2b: Predict the class of the image using VGG 16
Apply the pre-trained VGG 16 model to predict the class label of the loaded image.
Step 3: Load a few images in your notebook and predict the class
Load multiple images into your notebook, preprocess them similarly, and predict their class labels using the pre-trained VGG 16 model.
Step 4: Explore how to remove the last layer of the VGG model
Investigate methods to remove the last layer of the VGG 16 model, which is typically the softmax layer for class prediction, in order to adapt it for other tasks.
Step 5: Add a few layers to the VGG 16 model
Extend the VGG 16 model by adding additional layers (e.g., dense layers) to modify its architecture for specific requirements.
Step 6: Add binary classification data and compile the model
Integrate binary classification data with the modified VGG 16 model and compile it with appropriate loss function, optimizer, and metrics.
Step 7: Train the new model for binary classification of images
Train the modified VGG 16 model using the binary classification data, and evaluate its performance.
Step 8: Define the layers which are trainable
Specify which layers of the modified VGG 16 model are trainable during the training process, and which layers are frozen to retain pre-learned features.
# import libraries
import numpy as np
from keras.preprocessing.image import img_to_array
from keras.applications import VGG16
from keras.applications.vgg16 import preprocess_input, decode_predictions
from keras.models import Model
from keras.layers import Dense, Dropout
from keras.optimizers import Adam
from keras.layers import Flatten
from keras.utils import to_categorical
from PIL import Image
from keras.preprocessing import image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from keras.preprocessing.image import load_img, ImageDataGenerator
Task 2: Load the VGG 16 model in your notebook and print the summary of the model.
a. Load an image from file and pre-process it to prepare it to be applied to the model.
# Load the VGG16 model
model = VGG16(weights='imagenet', include_top=True)
model.summary()
Model: "vgg16"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input_1 (InputLayer) [(None, 224, 224, 3)] 0
block1_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 224, 224, 64) 1792
block1_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 224, 224, 64) 36928
block1_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 112, 112, 64) 0
block2_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 112, 112, 128) 73856
block2_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 112, 112, 128) 147584
block2_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 56, 56, 128) 0
block3_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 295168
block3_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 590080
block3_conv3 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 590080
block3_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 28, 28, 256) 0
block4_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 1180160
block4_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 2359808
block4_conv3 (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 2359808
block4_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 0
block5_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 2359808
block5_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 2359808
block5_conv3 (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 2359808
block5_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 7, 7, 512) 0
flatten (Flatten) (None, 25088) 0
fc1 (Dense) (None, 4096) 102764544
fc2 (Dense) (None, 4096) 16781312
predictions (Dense) (None, 1000) 4097000
=================================================================
Total params: 138357544 (527.79 MB)
Trainable params: 138357544 (527.79 MB)
Non-trainable params: 0 (0.00 Byte)
_________________________________________________________________
image_path = r"F:\New_Laptop_Documents\NMIMS_College_Docs\3rd_Year\1st_Semester\DL\Practicals\Lab9\Nitro_Wallpaper_5000x2813.jpg"
image = load_img(image_path, target_size=(224, 224))
image = img_to_array(image)
image = preprocess_input(image)
b. Predict the class of the image using VGG 16
predictions = model.predict(image.reshape(1, 224, 224, 3))
decoded_predictions = decode_predictions(predictions, top=5)[0]
1/1 [==============================] - 0s 335ms/step
for i, (imagenet_id, label, score) in enumerate(decoded_predictions):
print(f"{i + 1}: {label} ({score:.2f})")
1: sea_urchin (0.70)
2: sea_anemone (0.08)
3: theater_curtain (0.05)
4: lionfish (0.01)
5: daisy (0.01)
Task 3: Load a few images in your notebook and predict the class of the image using the pre- trained model
# Step 3: Load a few images and predict their classes
image_paths = ['Image_1.jpg', 'Image_2.jpg', 'Gaussian.jpeg', 'Salt_Pepper.jpg']
for image_path in image_paths:
# Load an image from file
image = load_img(image_path, target_size=(224, 224))
image = img_to_array(image)
image = preprocess_input(image)
# Predict the class of the image using VGG16
predictions = model.predict(image.reshape(1, 224, 224, 3))
decoded_predictions = decode_predictions(predictions, top=5)[0]
print(f"Predictions for {image_path}:")
for i, (imagenet_id, label, score) in enumerate(decoded_predictions):
print(f"{i + 1}: {label} ({score:.2f})")
1/1 [==============================] - 0s 109ms/step
Predictions for Image_1.jpg:
1: alp (0.78)
2: geyser (0.15)
3: volcano (0.03)
4: valley (0.02)
5: cliff (0.02)
1/1 [==============================] - 0s 119ms/step
Predictions for Image_2.jpg:
1: groom (0.15)
2: suit (0.11)
3: bookcase (0.11)
4: wardrobe (0.08)
5: sliding_door (0.05)
1/1 [==============================] - 0s 123ms/step
Predictions for Gaussian.jpeg:
1: shovel (0.08)
2: bucket (0.07)
3: great_white_shark (0.07)
4: ashcan (0.07)
5: mask (0.03)
1/1 [==============================] - 0s 115ms/step
Predictions for Salt_Pepper.jpg:
1: book_jacket (0.90)
2: comic_book (0.03)
3: web_site (0.02)
4: envelope (0.00)
5: scuba_diver (0.00)
Task 4: Explore how to remove the last layer of the VGG model.
model_without_last_layer = Model(inputs=model.input, outputs=model.layers[-2].output)
model_without_last_layer.summary()
Model: "model"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input_1 (InputLayer) [(None, 224, 224, 3)] 0
block1_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 224, 224, 64) 1792
block1_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 224, 224, 64) 36928
block1_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 112, 112, 64) 0
block2_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 112, 112, 128) 73856
block2_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 112, 112, 128) 147584
block2_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 56, 56, 128) 0
block3_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 295168
block3_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 590080
block3_conv3 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 590080
block3_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 28, 28, 256) 0
block4_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 1180160
block4_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 2359808
block4_conv3 (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 2359808
block4_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 0
block5_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 2359808
block5_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 2359808
block5_conv3 (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 2359808
block5_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 7, 7, 512) 0
flatten (Flatten) (None, 25088) 0
fc1 (Dense) (None, 4096) 102764544
fc2 (Dense) (None, 4096) 16781312
=================================================================
Total params: 134260544 (512.16 MB)
Trainable params: 134260544 (512.16 MB)
Non-trainable params: 0 (0.00 Byte)
_________________________________________________________________
Task 5: Add a few layers to the VGG 16 model.
# Define the number of classes (2 for binary classification)
num_classes = 2
custom_top_layer = Dense(256, activation='relu')(model_without_last_layer.output)
custom_top_layer = Dropout(0.5)(custom_top_layer)
output_layer = Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax')(custom_top_layer)
new_model = Model(inputs=model_without_last_layer.input, outputs=output_layer)
new_model.summary()
Model: "model_1"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input_1 (InputLayer) [(None, 224, 224, 3)] 0
block1_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 224, 224, 64) 1792
block1_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 224, 224, 64) 36928
block1_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 112, 112, 64) 0
block2_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 112, 112, 128) 73856
block2_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 112, 112, 128) 147584
block2_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 56, 56, 128) 0
block3_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 295168
block3_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 590080
block3_conv3 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 590080
block3_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 28, 28, 256) 0
block4_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 1180160
block4_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 2359808
block4_conv3 (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 2359808
block4_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 0
block5_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 2359808
block5_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 2359808
block5_conv3 (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 2359808
block5_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 7, 7, 512) 0
flatten (Flatten) (None, 25088) 0
fc1 (Dense) (None, 4096) 102764544
fc2 (Dense) (None, 4096) 16781312
dense (Dense) (None, 256) 1048832
dropout (Dropout) (None, 256) 0
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 2) 514
=================================================================
Total params: 135309890 (516.17 MB)
Trainable params: 135309890 (516.17 MB)
Non-trainable params: 0 (0.00 Byte)
_________________________________________________________________
Task 6: Add binary classification data and compile the model.
new_model.compile(optimizer=Adam(learning_rate=0.0001), loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
Task 7 and 8: Train the new model for binary classification of images. Further Predict for a random image.
def predict(img1):
plt.imshow(img1)
x = image.img_to_array(img1)
x = np.expand_dims(x,axis=0)
x - preprocess_input(x)
img_class = model.predict(x)
predict_class = decode_predictions(img_class)
print(predict_class)
img_path1 = "Image_1.jpg"
img1 = image.load_img(img_path1, target_size = (224,224))
img_path2 = 'Image_2.jpg'
img2 = image.load_img(img_path2, target_size = (224,224))
img_path3 = 'Gaussian.jpeg'
img3 = image.load_img(img_path3, target_size = (224,224))
img_path4 = 'Salt_Pepper.jpeg'
img4 = image.load_img(img_path3, target_size = (224,224))
data = []
data.append(np.array(img1))
data.append(np.array(img2))
data.append(np.array(img3))
data.append(np.array(img4))
data = np.array(data)
data
array([[[[ 51, 52, 54],
[ 52, 53, 55],
[ 52, 53, 55],
...,
[118, 101, 73],
[110, 94, 71],
[ 96, 84, 70]],
[[ 50, 51, 53],
[ 51, 52, 54],
[ 51, 52, 54],
...,
[121, 101, 74],
[112, 94, 72],
[ 97, 85, 69]],
[[ 50, 51, 53],
[ 51, 52, 54],
[ 51, 52, 54],
...,
[123, 104, 74],
[116, 98, 74],
[100, 87, 71]],
...,
[[ 13, 13, 11],
[ 10, 12, 11],
[ 13, 15, 14],
...,
[ 15, 16, 18],
[ 17, 18, 20],
[ 14, 18, 21]],
[[ 8, 8, 8],
[ 17, 17, 19],
[ 8, 8, 8],
...,
[ 8, 12, 15],
[ 14, 18, 21],
[ 26, 30, 33]],
[[ 16, 16, 16],
[ 13, 13, 15],
[ 47, 47, 47],
...,
[ 8, 12, 15],
[ 33, 37, 40],
[ 11, 12, 14]]],
[[[148, 112, 38],
[157, 121, 33],
[175, 140, 48],
...,
[187, 146, 67],
[169, 128, 46],
[199, 149, 78]],
[[140, 104, 30],
[146, 109, 21],
[169, 133, 39],
...,
[198, 155, 77],
[182, 137, 54],
[208, 155, 85]],
[[136, 101, 17],
[163, 126, 38],
[160, 123, 34],
...,
[197, 151, 73],
[183, 136, 54],
[216, 162, 92]],
...,
[[124, 87, 9],
[155, 117, 36],
[168, 128, 40],
...,
[183, 133, 62],
[180, 128, 52],
[172, 115, 44]],
[[106, 68, 0],
[159, 121, 40],
[174, 134, 46],
...,
[180, 130, 57],
[180, 129, 50],
[167, 110, 41]],
[[119, 80, 3],
[159, 118, 36],
[169, 129, 41],
...,
[184, 135, 59],
[190, 138, 62],
[172, 115, 48]]],
[[[188, 188, 188],
[161, 161, 161],
[151, 151, 151],
...,
[191, 191, 191],
[174, 174, 174],
[149, 149, 149]],
[[179, 179, 179],
[174, 174, 174],
[133, 133, 133],
...,
[158, 158, 158],
[172, 172, 172],
[ 66, 66, 66]],
[[175, 175, 175],
[149, 149, 149],
[138, 138, 138],
...,
[183, 183, 183],
[185, 185, 185],
[214, 214, 214]],
...,
[[106, 106, 106],
[107, 107, 107],
[ 92, 92, 92],
...,
[147, 147, 147],
[159, 159, 159],
[167, 167, 167]],
[[106, 106, 106],
[103, 103, 103],
[ 92, 92, 92],
...,
[151, 151, 151],
[168, 168, 168],
[157, 157, 157]],
[[ 93, 93, 93],
[122, 122, 122],
[ 96, 96, 96],
...,
[148, 148, 148],
[157, 157, 157],
[156, 156, 156]]],
[[[188, 188, 188],
[161, 161, 161],
[151, 151, 151],
...,
[191, 191, 191],
[174, 174, 174],
[149, 149, 149]],
[[179, 179, 179],
[174, 174, 174],
[133, 133, 133],
...,
[158, 158, 158],
[172, 172, 172],
[ 66, 66, 66]],
[[175, 175, 175],
[149, 149, 149],
[138, 138, 138],
...,
[183, 183, 183],
[185, 185, 185],
[214, 214, 214]],
...,
[[106, 106, 106],
[107, 107, 107],
[ 92, 92, 92],
...,
[147, 147, 147],
[159, 159, 159],
[167, 167, 167]],
[[106, 106, 106],
[103, 103, 103],
[ 92, 92, 92],
...,
[151, 151, 151],
[168, 168, 168],
[157, 157, 157]],
[[ 93, 93, 93],
[122, 122, 122],
[ 96, 96, 96],
...,
[148, 148, 148],
[157, 157, 157],
[156, 156, 156]]]], dtype=uint8)
targets = [0, 0, 1]
targets = to_categorical(targets, num_classes=2)
image_paths = [r"F:\New_Laptop_Documents\NMIMS_College_Docs\3rd_Year\1st_Semester\DL\Practicals\Lab9\Image_1.jpg", r"F:\New_Laptop_Documents\NMIMS_College_Docs\3rd_Year\1st_Semester\DL\Practicals\Lab9\Image_2.jpg", r"F:\New_Laptop_Documents\NMIMS_College_Docs\3rd_Year\1st_Semester\DL\Practicals\Lab9\Gaussian.jpeg", r"F:\New_Laptop_Documents\NMIMS_College_Docs\3rd_Year\1st_Semester\DL\Practicals\Lab9\Salt_Pepper.jpg"]
model3 = VGG16(weights='imagenet', include_top=False, input_shape=(224, 224, 3))
x = model3.output
x = Flatten()(x)
x = Dense(1024, activation='relu')(x)
predictions = Dense(2, activation='softmax')(x)
model3 = Model(inputs=model3.input, outputs=predictions)
model3.compile(optimizer=Adam(learning_rate=0.0001), loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
def preprocess_img(img_path, target_size=(224, 224)):
img = image.load_img(img_path, target_size=target_size)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
x = image.img_to_array(img)
x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=0)
x = preprocess_input(x)
return x
def predict_class(model, img_path):
x = preprocess_img(img_path)
prediction = model.predict(x)
class_label = np.argmax(prediction)
probabilities = prediction[0] * 100
if class_label == 0:
print(f"The image is predicted to belong to the first class with {probabilities[0]:.2f}% probability.")
else:
print(f"The image is predicted to belong to the second class with {probabilities[1]:.2f}% probability.")
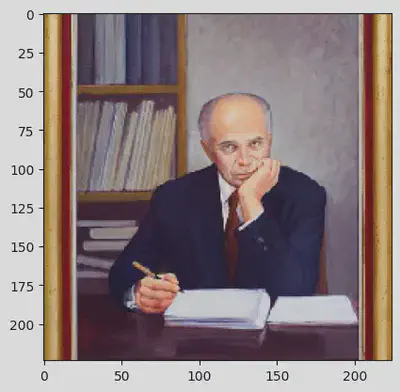
predict(img2)
1/1 [==============================] - 0s 128ms/step
[[('n02870880', 'bookcase', 0.19360466), ('n02883205', 'bow_tie', 0.053831667), ('n02871525', 'bookshop', 0.049464714), ('n04589890', 'window_screen', 0.048883837), ('n04005630', 'prison', 0.030654741)]]
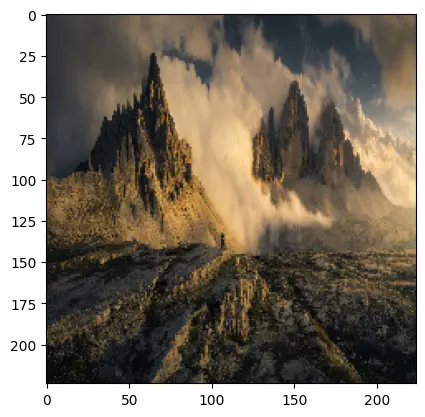
predict(img1)
1/1 [==============================] - 0s 113ms/step
[[('n09193705', 'alp', 0.4756926), ('n09288635', 'geyser', 0.31268018), ('n09246464', 'cliff', 0.07910416), ('n09472597', 'volcano', 0.0679643), ('n09468604', 'valley', 0.021801975)]]
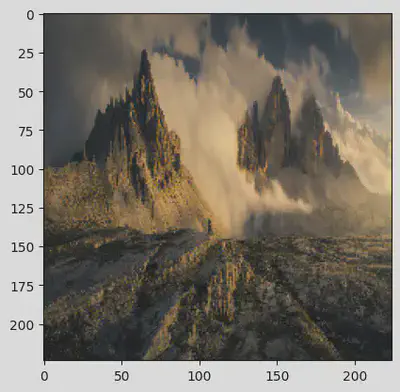
predict(img3)
1/1 [==============================] - 0s 113ms/step
[[('n02909870', 'bucket', 0.075282775), ('n02747177', 'ashcan', 0.06954469), ('n04208210', 'shovel', 0.06564177), ('n03388043', 'fountain', 0.034990232), ('n03724870', 'mask', 0.032282088)]]
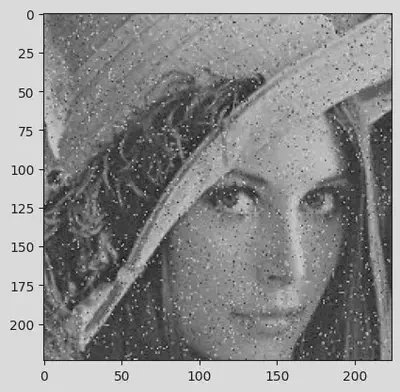
predict(img4)
1/1 [==============================] - 0s 117ms/step
[[('n02909870', 'bucket', 0.075282775), ('n02747177', 'ashcan', 0.06954469), ('n04208210', 'shovel', 0.06564177), ('n03388043', 'fountain', 0.034990232), ('n03724870', 'mask', 0.032282088)]]
Experiment Conclusion
In this student experiment, we explored transfer learning using the VGG16 model for binary image classification. The key highlights are:
Data Prep: We resized and preprocessed the MNIST dataset to fit the VGG16 model’s input requirements (224x224x3).
Model: We utilized VGG16, a pre-trained deep learning model, for its transfer learning capabilities.
Customization: Custom layers were added for binary classification (0 or 1), tailoring the model to our task.
Training: We trained the model on our data, adjusting labels for binary classification.
Fine-Tuning: By selectively unfreezing VGG16 layers, we fine-tuned the model for better performance.
In summary, this experiment introduced transfer learning with VGG16 as a valuable approach for students. It showcases the power of leveraging pre-trained models for efficient image classification and how fine-tuning can optimize performance. It’s a strong foundation for deeper exploration in deep learning and computer vision.